Although Botox® is widely known for its cosmetic applications, there are many ways Botox® can be used to treat both moderate and severe medical conditions. Doctors have only begun to discover what Botox® is capable of treating and patients everywhere are benefiting from these discoveries.
So, what are the medical uses of Botox®? Botox® has been found to treat many conditions related to muscular and nerve issues, such as Bell’s Palsy, enlarged prostate, gastroparesis, excessive sweating, teeth grinding, rosacea, migraine headaches, eye disorders, depression, and more.
WHAT IS BOTOX®?
Botox is a protein, made from Botulinum Toxin A, which is the bacterium produced by Clostridium botulinum. It is administered in small doses to areas of concern in order to temporarily smooth out the skin and prevent further wrinkles from appearing. Regular injections of Botox® can cause certain muscles to move less frequently, this can lead to smoother skin and the injection of less Botox® over time. This treatment is quick, minimally invasive and requires no downtime.
THE MEDICAL BENEFITS OF BOTOX®
The first medical application of Botulinum Toxin A was created to treat the condition of crossed eyes with a non-invasive and painless treatment. Nearly two decades later, doctors would begin using Botox® for a wide range of cosmetic treatments.
The cosmetic application of the neurotoxin was only seen after successful trials on monkeys and it was later tested on patients with strabismus. Researchers noticed that the injections also led to fewer lines in the area between the eyes, the glabella. While the cosmetic market for Botox® has exploded since the 90s, doctors have also experimented with its important role in various muscular and nerve conditions.
HOW IS BOTOX® APPLIED?
During the treatment, the doctor or nurse injects the necessary amount of Botox® into the muscle tissue. Patients should feel little to no pain depending on the area of the injection site, their general pain threshold, and whether any topical anesthetic is applied to the skin prior to the treatment.
While there are some immediate results after the injection, it typically takes 2-3 days before you will see the full effects of the treatment. Your body needs time to fully absorb the Botox® as it blocks the signals between the nerves and the muscles in order to prevent movement.
POSSIBLE BOTOX® SIDE EFFECTS
While some Botox® treatments may have more specific side effects, there are a few possible low-pain side effects that may occur with Botox®. These may potentially include:
- Muscle soreness
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Fever
- Nausea
These side effects are generally short-lived and should disappear a few hours after the treatment.
MEDICAL CONDITIONS BOTOX® CAN TREAT
BELL’S PALSY
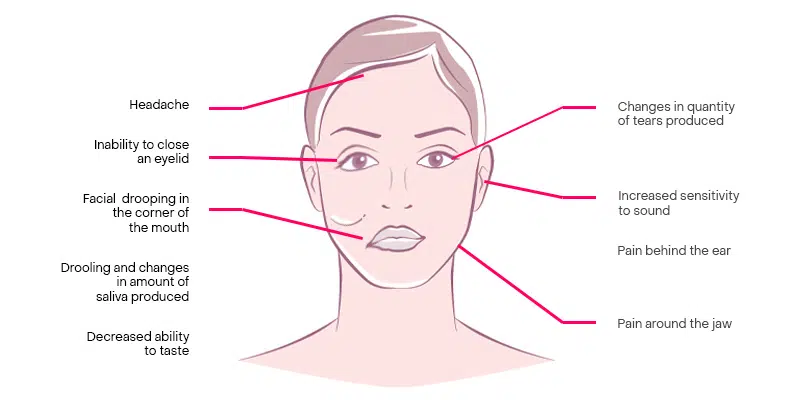
How can Botox® help treat Bell’s Palsy? As Bell’s Palsy is a condition of the facial muscles, Botox® is the perfect medication for intervention in patients experiencing long-term or permanent facial paralysis.
As these muscles become hyperactive during facial nerve paralysis, Botox® helps to relax the automatic muscle movements and the unwanted tension underneath the face. This helps faces return to a normal look, with results per treatment lasting up to 4 months.
ENLARGED PROSTATE
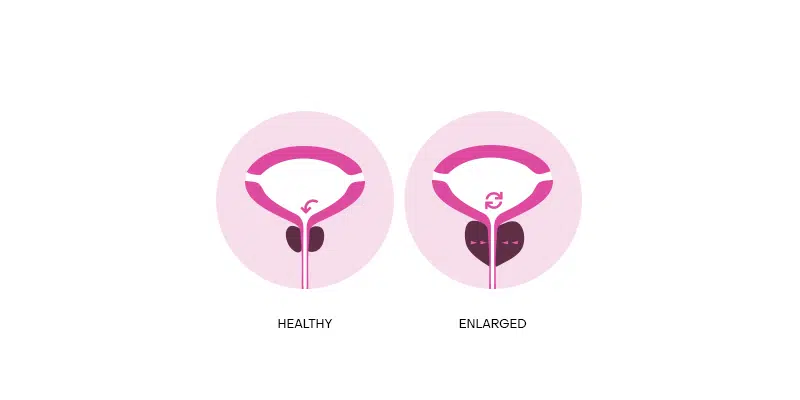
How can Botox® help treat enlarged prostate? Some doctors now treat enlarged prostate with Botox®, which has been found to drastically improve the quality of life of patients with enlarged prostate (with some effects lasting up to a year after Botox® treatment).
Through a process known as apoptosis, Botox® reduces the enlarged prostate gland by killing the prostate cells slowly. This allows the urine to pass more freely from the bladder through the urethra.
GASTROPARESIS
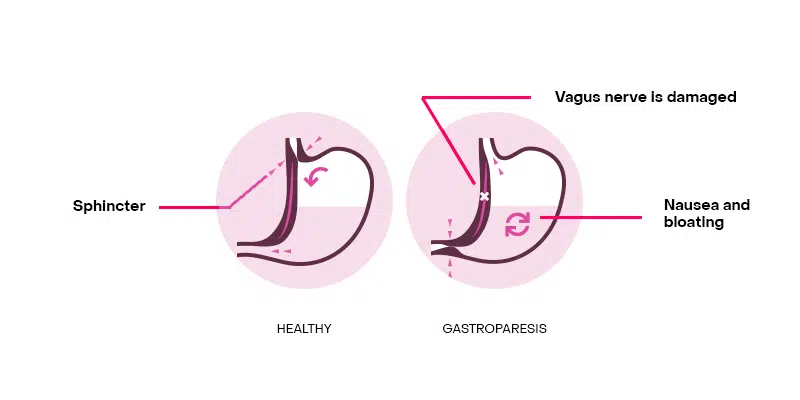
How can Botox® help treat gastroparesis? Part of the problem of gastroparesis involves spasms coming from a ring of muscles in the stomach known as the pyloric sphincter. This ring of muscles, also known as the pylorus, is involved with food passage from the stomach to the small intestine. A patient suffering gastroparesis experiences muscle spasm in the pylorus, which make it more difficult to empty the stomach.
Botox® injected into the pylorus relaxes these muscles, allowing the food transfer to occur without difficulty. A single treatment of Botox® has the potential to improve gastroparesis symptoms for up to 6 months!
HYPERHIDROSIS (EXCESSIVE SWEATING)
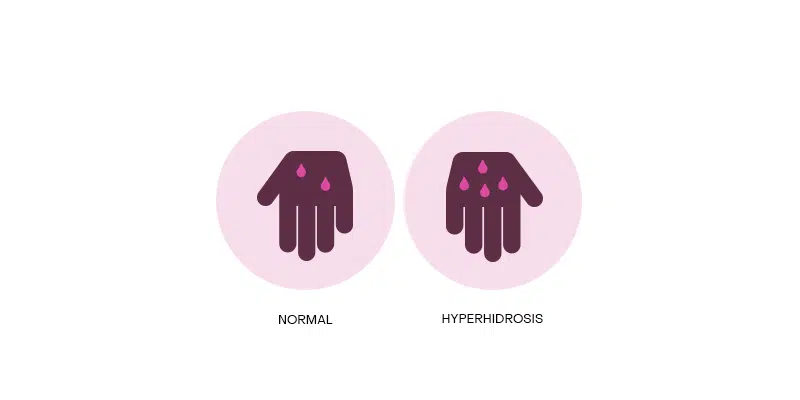
What causes hyperhidrosis? There are two kinds: Primary idiopathic hyperhidrosis, which has no single obvious cause, and secondary hyperhidrosis, in which the excessive sweating is a side effect of another condition, such as gout, tumor, hyperthyroidism, or obesity.
How can Botox® help treat hyperhidrosis? Sweating is the body’s natural response to the outside temperature. When it feels a higher temperature, it sends signals to the sweat glands to begin sweating. However, some people just have more active nerves than others, naturally or as a side effect of another condition, which leads to an excessive production of sweat.
Botox® is injected in the areas of excessive sweating, which paralyzes the nerves responsible for beginning sweat production. Results are so effective that after the Botox® has fully paralyzed the nerves, patients can experience complete dryness for several months.
TEETH GRINDING
How does Botox® help treat teeth grinding? Patients suffering stubborn bruxism have difficulty treating it, as there are no recognized trusted treatments to cure bruxism. Generally, patients are advised to wear mouthguards at night until the bruxism passes (if it ever does).
However, more and more doctors are turning to Botox® to treat teeth grinding. When injected directly into the jaw’s chewing muscles, or masseters, Botox® has been found to dramatically reduce nighttime teeth clenching and grinding in patients with bruxism. After relaxing the jaw’s chewing muscles, patients are far less likely to unconsciously chew and grind in their sleep.
ROSACEA
How does Botox® help treat rosacea? The blood vessels in individuals with rosacea generally become dilated when they are triggered, leading to the extreme redness and flushing on the face. Botox® helps to treat rosacea by paralyzing these blood vessels, prohibiting them from dilating.
With Botox® injected into the upper layers of the facial skin, it can interact directly with the blood vessels that cause facial flushing. Once paralyzed by the Botox®, the blood flow surges on the face lose their excess visibility. Like with other Botox® treatments, these results can last for months before patients need another session to keep up the desired results.
MUSCLE SPASTICITY

How does Botox® help treat muscle spasticity? While Botox® doesn’t help the direct relationship between the central nervous system and the muscles, it can assist the brain in getting its signals through to an unresponsive muscle set.
Botox® injected in the areas with muscles suffering spasticity can help to relax the muscles, making it easier for the individual to normally move and contract these muscles without difficulty.
URINARY INCONTINENCE
How does Botox® help treat urinary incontinence? Botox® can treat urinary incontinence by taking away the bladder’s unwanted contractions. The Botox® should be injected straight into the bladder, where it blocks the neurotransmitters operating between the bladder muscle and the bladder.
This prevents the bladder from contracting on its own, allowing patients to have greater control over their bladder. Results can last up to six months before patients must undergo another treatment.
MIGRAINE HEADACHES
How does Botox® help treat migraine headaches? While most medical uses for Botox® are off-label, Botox® injections for migraines is actually Health Canada and FDA-approved. This is most recommended for patients who experience headaches for 15 days or more every month.
For treatment, Botox® is injected around the nerve endings in the head that lead to migraines. The neurotoxin then paralyzes these nerve endings, blocking communication between the chemicals and the brain’s headache pain networks. Patients can experience relief from headaches for up to 10-12 weeks after just a single treatment.
DEPRESSION

How can Botox® help treat depression? Several studies over the course of the last two decades have found Botox® to be very effective at treating depression, alone or when paired with the proper antidepressant medication. The treatment involves injecting the glabellar frown lines – the lines between the eyes, above the nose – with Botox®, clearing them up.
Researchers suggest that the cause for the effectiveness of this treatment is due to a mechanism known as “facial feedback”. We are influenced by our facial expressions, and the angrier, sadder, and more negative we feel, the more pronounced our glabellar frown lines become. By injecting those lines with Botox®, they gradually start to disappear. And as we notice the disappearance of those lines between our eyes, over time our levels of depression naturally begin to improve.
CHRONIC NECK PAIN

How can Botox® help treat chronic neck pain? Some cases of neck pain are caused by muscles that are chronically contracted or tense. Doctors begin by identifying the tense muscles, and then injecting Botox® in the surrounding areas to target them. The Botox® causes the muscles to relax, helping to ease the chronic neck pain.
Patients generally accompany these Botox® injections for chronic neck pain with various forms of physical therapy.
CEREBRAL PALSY
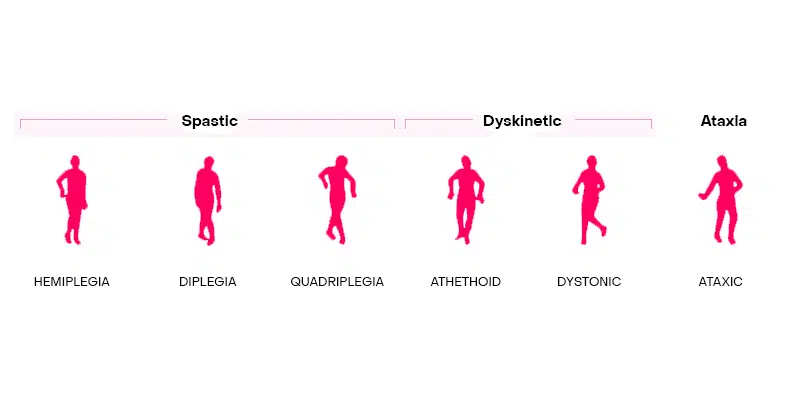
How can Botox® help treat cerebral palsy? Individuals and especially children suffering from cerebral palsy struggle with muscle spasticity caused by involuntary muscle stiffness. Botox® helps to ease muscle spasticity of cerebral palsy by easing the patient’s muscle stiffness.
Immediate benefits of Botox® include fewer spastic movements, an easier time walking, less overall body pain, and greater range of motion.
CERVICAL DYSTONIA
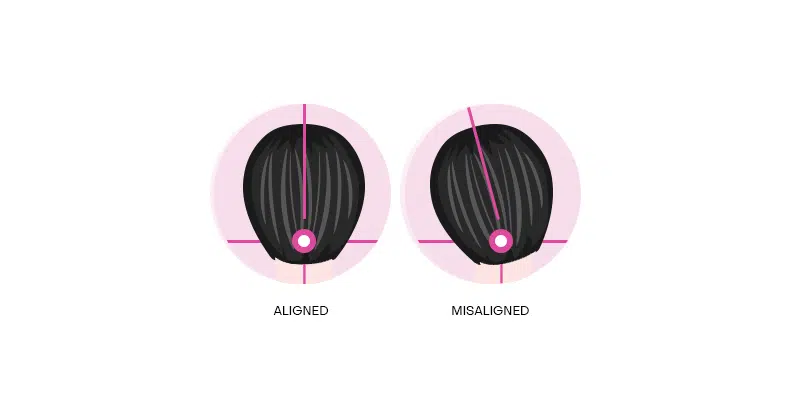
How can Botox® help treat cervical dystonia? The involuntary neck muscle contractions individuals with cervical dystonia experience are a result of signals from the brain automatically forcing them to spasm or bend.
In cases of cervical dystonia, Botox® is injected into the neck area, where the patient most commonly experiences the involuntary contraction. The Botox® paralyzes the muscles and nerve endings in this area, leading to a dramatic reduction of involuntary contractions for up to 3 months every session.
EYE DISORDERS
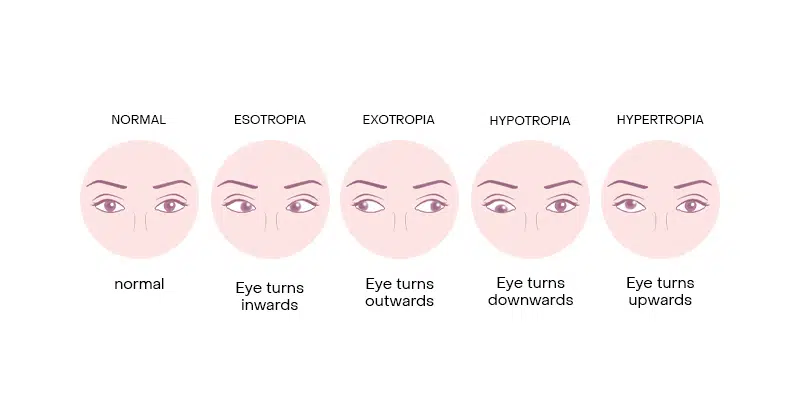
How can Botox® help treat eye disorders? The first medical application of Botox® to be tested on humans and approved by the FDA was actually for strabismus, or crossed eyes, back in the late 70s.
Botox® can be injected near the eye area, generally in the glabellar lines, helps to relax the muscles that control the eye movement, helping individuals suffering from various eye muscle disorders.
BOTOX® BEYOND COSMETICS
The versatility of Botox® proves that it goes beyond erasing fine lines and smoothing out wrinkles. When applied by a knowledgeable professional, patients can harness the power of this super toxin to control and treat both major and minor inconveniences, one injection at a time.
We are Canada’s leader in Botox® treatments, so if you’re interested in seeing what this procedure can do for you, look no further than Skin Vitality. Our clinics are staffed with professional Botox® injectors that are ready to listen to what you need and help you achieve the right results. We’ll help you figure out exactly what your problem areas are in order to get the best results from your Botox® treatments. We will also be able to help you with any other questions or concerns you may have. We have 9 locations in the GTA with top-of-the-line cosmetic treatments. Are you wondering if Botox the right medical treatment for you? Talk to us today, and learn how Botox® can help change your life.
Sources:
- How BOTOX® works
- BOTOX®
- What are the benefits?
- Could Botox stop teeth grinding?
- There’s A New Way To Treat Rosacea — & It Might Surprise You
- OnabotulinumtoxinA Injections (Botox®)
- Men With Enlarged Prostate Can Benefit From Botox Injections Up To A Year After Treatment
- Botox as Incontinence Therapy
- Using Botulinum Toxin for Muscle Spasticity
- Botox May Ease Chronic Neck Pain

